In today’s rapidly evolving digital landscape, organizations increasingly recognize that defending against sophisticated cyber threats in isolation is no longer viable.
Recent developments in collaborative threat intelligence sharing frameworks demonstrate how the cybersecurity community is uniting to combat these challenges collectively.
Recent Advancements in Threat Intelligence Platforms
The open-source threat intelligence platform MISP released a new version in May 2025, introducing significant security fixes, improvements to attribute validation, and enhanced UI features for event views and analyst workflows.
This update represents a critical advancement for the platform, which has become a cornerstone for threat intelligence sharing since its inception in 2011.
MISP is designed by and for incident analysts, security and ICT professionals, and malware reversers to support their day-to-day operations and share structured information efficiently.
The project continues to evolve, though its ambitious next major milestone is past due. This reflects the complexity and ongoing demand for robust threat intelligence solutions.
ISACs Leading Cross-Sector Collaboration
Information Sharing and Analysis Centers (ISACs) facilitate threat intelligence exchange. The Financial Services ISAC (FS-ISAC) is preparing for several key events, including the 2025 EMEA Summit in Brussels and multiple regional member forums in late May.
These sector-specific communities provide trusted environments where organizations can share sensitive threat data using protocols like the Traffic Light Protocol (TLP), which classifies information into four categories- RED, AMBER, GREEN, and CLEAR- to control how widely information can be distributed.
This structured approach ensures that sensitive intelligence reaches stakeholders without risking unnecessary exposure.
European Union Enhancing Cybersecurity Posture
The European Union Agency for Cybersecurity (ENISA) published its latest threat landscape assessment in March 2025, identifying seven prime cybersecurity threats: threats against availability, ransomware, threats against data, malware, social engineering, information manipulation and interference, and supply chain attacks.
ENISA’s report highlights concerning trends, including zero-day exploits, complex DDoS attacks, expanding hacktivism around significant events, AI-enabled disinformation and deepfakes, and ongoing regional conflicts shaping the cybersecurity landscape.
These insights drive collaborative defense strategies across EU member states, encouraging a united response to increasingly complex threats.
Benefits of Collaborative Intelligence Frameworks
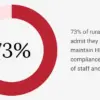
Organizations implementing collaborative threat intelligence frameworks are seeing tangible benefits. Bidirectional threat intelligence sharing allows for a two-way exchange of information, where both parties actively contribute to the conversation and foster a deeper understanding of evolving cyber risks.
The top advantages include faster threat detection and response, enhanced defense against emerging threats, and improved resource efficiency.
One financial institution reportedly saved hundreds of thousands daily by implementing a collaborative cyber fraud prevention framework.
By exchanging cyber threat information within a sharing community, organizations can leverage that community’s collective knowledge, experience, and capabilities to gain a more complete understanding of the threats they may face.
This collective approach has proven essential in staying ahead of adversaries and protecting critical assets.
Standardization Driving Interoperability
The adoption of standardized formats and protocols remains crucial for effective intelligence sharing.
The STIX (Structured Threat Information eXpression) and TAXII (Trusted Automated eXchange of Intelligence Information) standards continue to gain traction as they enable systems to exchange threat intelligence in a consistent, machine-readable format.
STIX provides a standard syntax so users can describe threats consistently by their motivations, abilities, capabilities, and responses, while TAXII offers the format through which threat intelligence data is transmitted.
These standards are helping organizations streamline their threat intelligence operations and ensure interoperability across platforms and sectors.
Challenges and Future Direction
Despite progress, implementing effective sharing frameworks remains challenging. Organizations must navigate concerns around data trust, integration difficulties, and confidentiality.
Establishing clear information-sharing rules that control the publication and distribution of threat information remains paramount.
Looking ahead, cyber threat intelligence frameworks are expected to continue evolving, adapting to the changing threat landscape and leveraging cutting-edge technologies to enhance their effectiveness.
Integrating artificial intelligence and machine learning capabilities will likely accelerate threat detection and analysis, while cross-sectoral collaboration becomes increasingly essential.
As cyber attacks grow more sophisticated, the security community’s ability to develop and maintain robust collaborative threat intelligence frameworks will be crucial in defending critical infrastructure and sensitive data against persistent adversaries.
Find this News Interesting! Follow us on Google News, LinkedIn, & X to Get Instant Updates!




.png
)
