A comprehensive new cybersecurity assessment has revealed that internet connectivity poses the most significant threat to industrial control systems (ICS) worldwide, with malicious activities targeting critical infrastructure through web-based attack vectors reaching unprecedented levels.
The latest quarterly threat landscape report covering the first quarter of 2025 demonstrates that internet-based threats have consistently outpaced all other attack sources, including email and removable media, across every global region monitored in the study.
The findings indicate that 21.9% of ICS computers globally experienced blocked malicious activities during the first quarter of 2025, a figure that has remained stubbornly consistent despite ongoing cybersecurity investments.
Regional variations paint a concerning picture, with Africa leading at 29.6% of affected systems, followed closely by South-East Asia at 29.1%, while Northern Europe maintained the lowest rate at 10.7%.
These disparities highlight significant gaps in cybersecurity maturity and infrastructure protection across different geographical areas.
Kaspersky analysts identified that internet threats manifest primarily through denylisted web resources, malicious scripts, phishing pages, web miners, and spyware applications that exploit system vulnerabilities when ICS computers maintain external connectivity.
The research team noted that whenever internet threats are detected and blocked on protected ICS systems, it indicates those systems had unauthorized or uncontrolled access to external services at the time of detection, representing a fundamental breach of operational technology security protocols.
The threat actors have increasingly sophisticated their approaches, utilizing command-and-control infrastructure distributed across compromised websites and leveraging content delivery networks to distribute malicious payloads.
Africa experienced the highest concentration of internet-based attacks at 12.76% of monitored systems, while South-East Asia followed at 12.32%, and South Asia recorded 10.83% of affected computers.
Russia demonstrated the most significant quarterly increase in internet threats, rising by 1.29 percentage points, followed by Central Asia with a 1.04 percentage point increase.
Industrial facilities across multiple sectors face heightened exposure due to the convergence of operational technology networks with internet-accessible systems, creating attack surfaces that threat actors actively exploit to deploy next-stage malware including ransomware, cryptocurrency miners, and advanced persistent threat tools.
Advanced Threat Distribution Mechanisms Through Compromised Web Infrastructure
The technical analysis reveals that cybercriminals have developed sophisticated distribution networks utilizing compromised legitimate websites and content delivery networks to bypass traditional security perimeters.
These attacks frequently begin with employees accessing seemingly benign web resources that have been weaponized with malicious scripts designed to fingerprint industrial systems and establish persistent access channels.
The malware deployment process typically involves multi-stage infections where initial JavaScript-based reconnaissance tools collect system information before downloading secondary payloads.
Threat actors particularly target outdated content management systems, with researchers observing a new wave of attacks specifically targeting websites built with outdated ASPRO templates for the Bitrix CMS platform.
These compromised sites serve as staging areas for delivering both browser-based and executable malware to industrial environments.

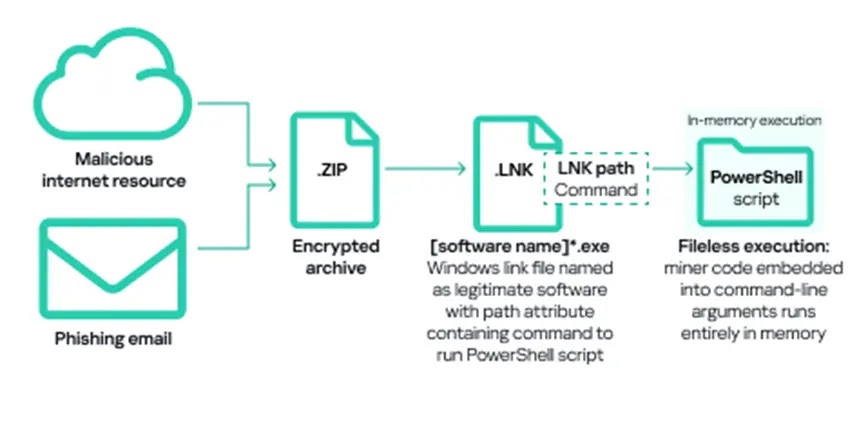
Modern attack chains increasingly utilize fileless execution techniques, where PowerShell scripts embedded in seemingly legitimate file shortcuts execute malicious cryptocurrency mining code directly in system memory.
.webp)
This approach helps threat actors evade traditional signature-based detection while maintaining persistence within industrial networks that often lack comprehensive endpoint monitoring capabilities.
The report emphasizes that organizations with insufficient network segmentation and inadequate internet access controls face exponentially higher risks, as demonstrated by the correlation between high internet threat percentages and elevated detection rates for self-propagating malware across affected regions.
Speed up and enrich threat investigations with Threat Intelligence Lookup! -> 50 trial search requests


.png
)
